What is a stroke?
A stroke happens when a blood vessel in your brain gets blocked and stops the flow of oxygenated blood to the brain. This is called an ischemic stroke.

Bursts or bleeds in or around the brain. This is called a hemorrhagic stroke.
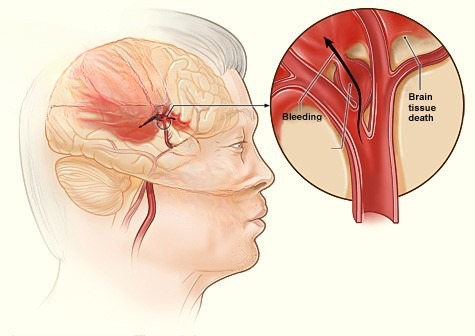
What happens during a stroke?
Blood brings oxygen and nutrients to the body. A burst or blocked blood vessel stops blood from reaching some parts of the brain. Blood that does not start flowing back to the brain within minutes can cause damage to the brain and the parts of the body it controls. The effects of a stroke will depend on where and how much of the brain was damaged and can affect how you think, see, move, feel and/or speak. Learn about the functions of the brain.
Some strokes happen while people are asleep. If you wake up with any of the following symptoms of a stroke, get medical help right away.
- numbness or weakness on one side of the body
- drooping of the face
- slurred or jumbled speech
- changes in vision, such as blurred or double vision
- sudden severe headache, usually with some of the other signs
- problems with balance
What is a Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)?
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) happens when there is a temporary stoppage of blood flow and oxygen to the brain. The symptoms are like a stroke but only lasts less than 24 hours. This is often called a mini-stroke. A TIA is an important warning sign of a possible stroke. It is a medical emergency that needs to be assessed and treated right away. Symptoms of a TIA may include:
- temporary weakness or numbness
- slurred speech, or
- trouble seeing clearly
What causes a stroke?
A stroke often happens without warning signs.
There are some things that make it more likely that someone will have a stroke:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Poorly managed diabetes
- Unhealthy eating habits
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Smoking or using tobacco products
- Not enough exercise
- Atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat)
Risk factors for stroke can be divided into two categories: risk factors you can’t change (non-modifiable risk factors) and risk factors you can change (modifiable risk factors). Modifiable risk factors can be controlled by medications, medical treatment, or lifestyle changes. Non-modifiable risk factors cannot be changed.
Modifiable Risk Factors
- Hypertension
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Diabetes
- Atrial fibrillation
- Sleep apnea
- Being overweight or obese
- Physical inactivity
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol and drug abuse
- Stress
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
- Advanced age
- Gender
- Family and medical history
- Ethnicity
- Prior stroke or TIA
Signs of a stroke
Are there warning signs before a stroke happens?
For most people a stroke happens suddenly. The signs of a stroke are:
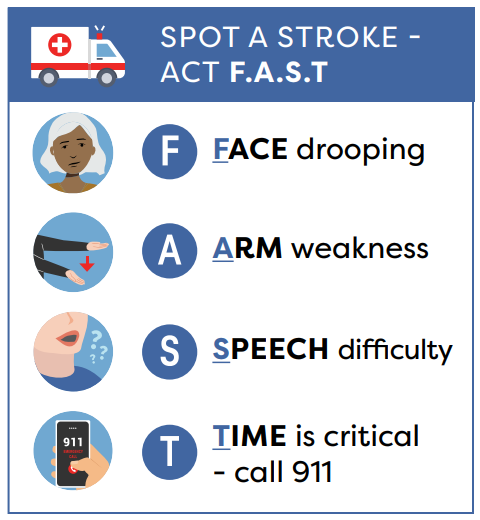
Stroke is a medical emergency. Spot a stroke – act F.A.S.T
If you notice any of these warning signs, call 911 right away!
Credit: Northwestern Ontario Regional Stroke Network